Data visualization with R
IASSL Workshop
Dr. Priyanga D. Talagala, University of Moratuwa
21-25, February, 2022


Tidy Workflow
Tidy Workflow
Tidy Workflow
The Datasaurus Dozen
library(datasauRus)library(ggplot2)datasaurus_dozen %>% ggplot(aes(x, y, color = dataset)) + geom_point(show.legend = FALSE) + facet_wrap(~dataset, ncol = 4)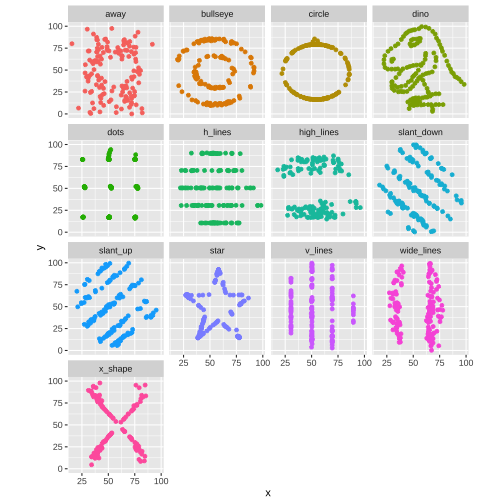
The Datasaurus Dozen
library(datasauRus)library(ggplot2)datasaurus_dozen %>% ggplot(aes(x, y, color = dataset)) + geom_point(show.legend = FALSE) + facet_wrap(~dataset, ncol = 4)| Summary statistics | |
|---|---|
| X Mean | 54.263 |
| Y Mean | 47.832 |
| X SD | 16.765 |
| Y SD | 26.935 |
| Corr. | -0.064 |
The Datasaurus was created by Alberto Cairo
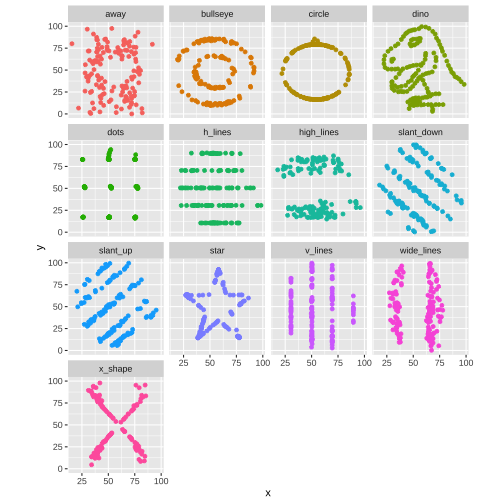
Never trust summary statistics ALONE
Never trust summary statistics ALONE
Always visualize your data
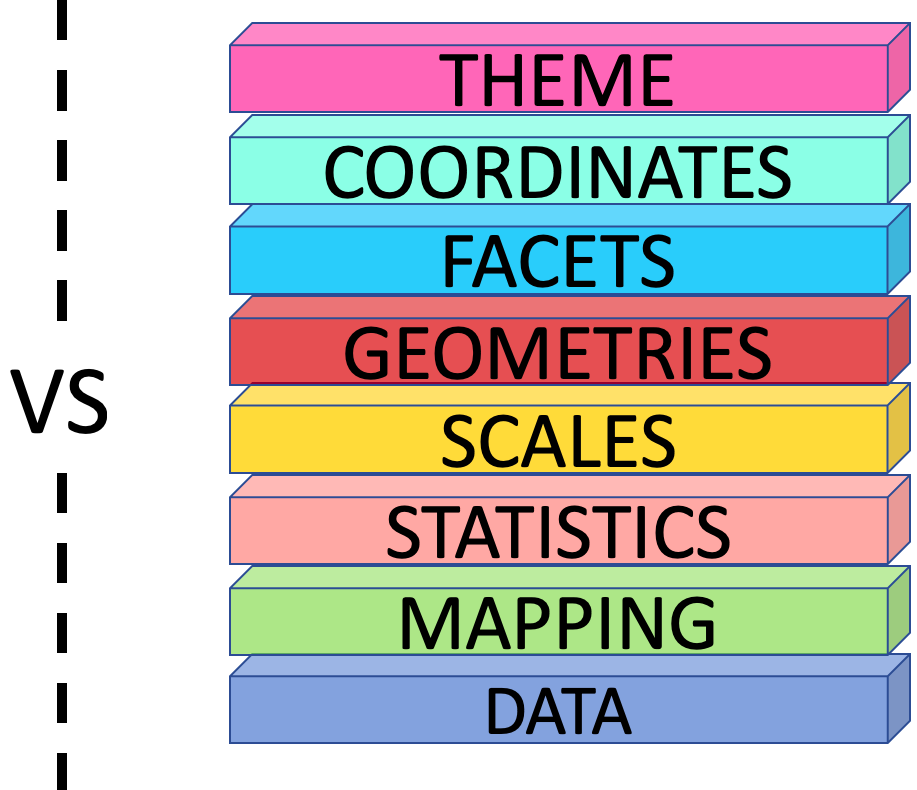
The Grammar of Graphics
The Book
The Grammar of Graphics

R Base Graphics
The Grammar of Graphics
Pie Chart
Line Chart
Bar Chart
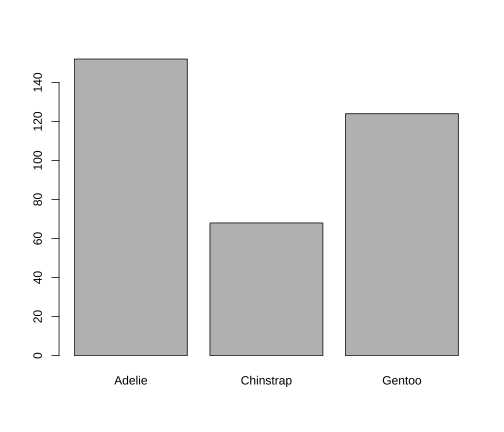
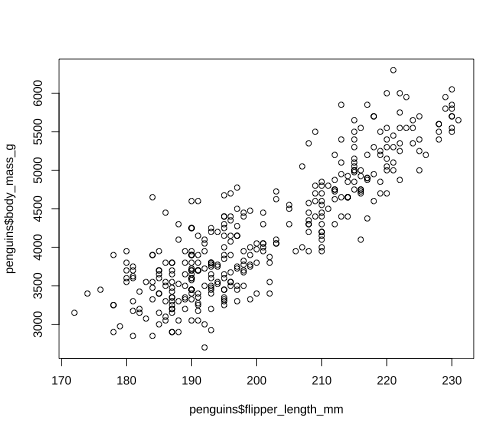
Scatterplot
The ggplot2 API

Which dataset to plot?

palmerpenguins data
The Palmer Archipelago penguins. Artwork by @allison_horst.


# A tibble: 6 × 8 species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_… body_mass_g sex <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct>1 Adelie Torge… 39.1 18.7 181 3750 male 2 Adelie Torge… 39.5 17.4 186 3800 fema…3 Adelie Torge… 40.3 18 195 3250 fema…4 Adelie Torge… NA NA NA NA <NA> 5 Adelie Torge… 36.7 19.3 193 3450 fema…6 Adelie Torge… 39.3 20.6 190 3650 male # … with 1 more variable: year <int>Rows: 344Columns: 8$ species <fct> Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adel…$ island <fct> Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgerse…$ bill_length_mm <dbl> 39.1, 39.5, 40.3, NA, 36.7, 39.3, 38.9, 39.2, 34.1, …$ bill_depth_mm <dbl> 18.7, 17.4, 18.0, NA, 19.3, 20.6, 17.8, 19.6, 18.1, …$ flipper_length_mm <int> 181, 186, 195, NA, 193, 190, 181, 195, 193, 190, 186…$ body_mass_g <int> 3750, 3800, 3250, NA, 3450, 3650, 3625, 4675, 3475, …$ sex <fct> male, female, female, NA, female, male, female, male…$ year <int> 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007…Which dataset to plot?
ggplot()
Which dataset to plot?
ggplot(data = penguins)
Mapping
Which columns to use for x and y?
ggplot(data = penguins, mapping = aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g))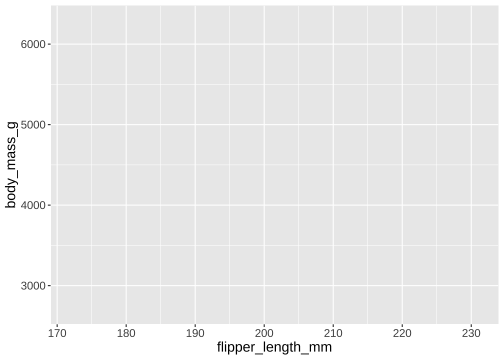
Geometries
How to draw the plot?
ggplot(data = penguins, mapping = aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point()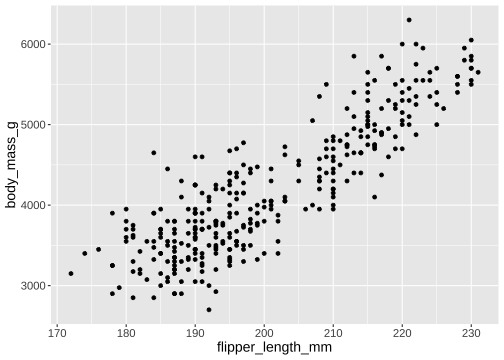
Data, Mapping and Geometries
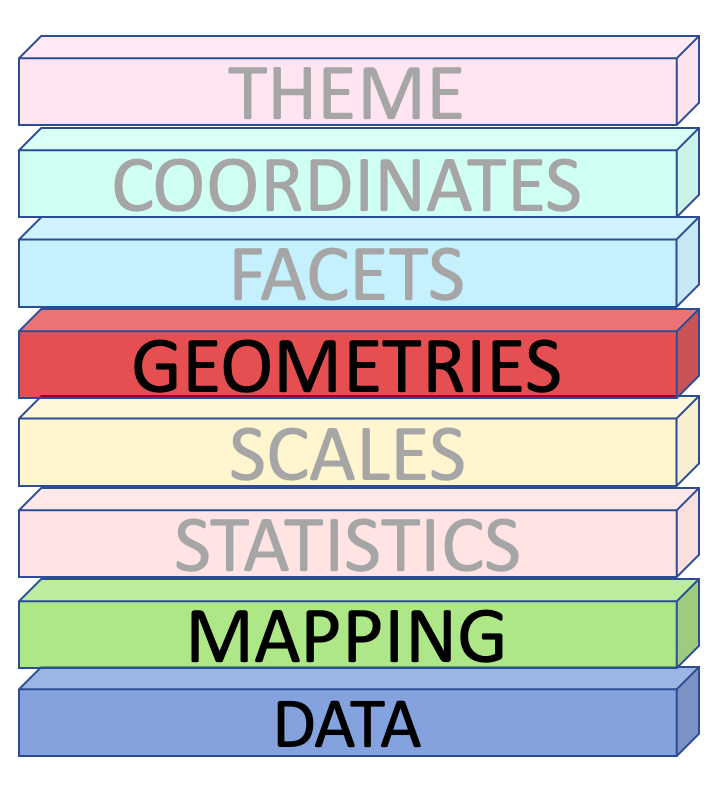
How to draw the plot?
ggplot(data = penguins) + geom_point(mapping = aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g))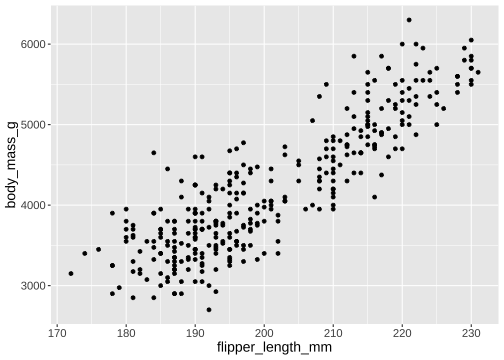
How to draw the plot?
ggplot() + geom_point(mapping = aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g), data = penguins)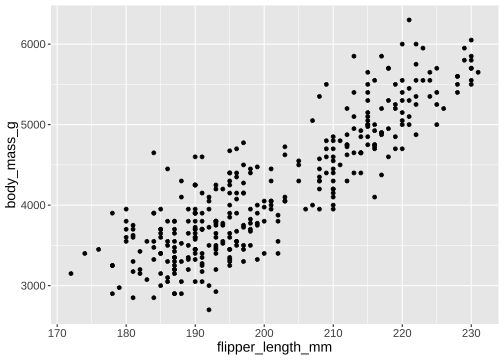
Mapping Colours
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point( aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species, shape = species))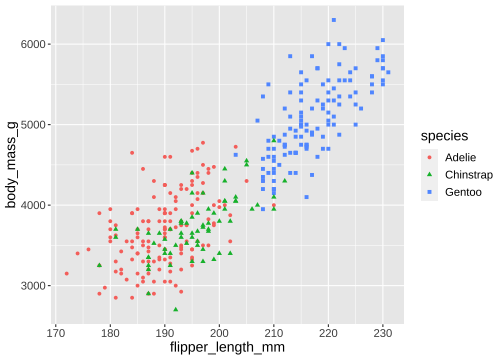
Mapping Colours
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point( aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, colour = flipper_length_mm < 205))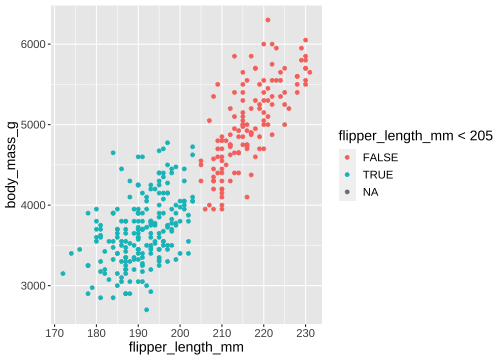
Setting Colours
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point( aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g), colour = 'purple')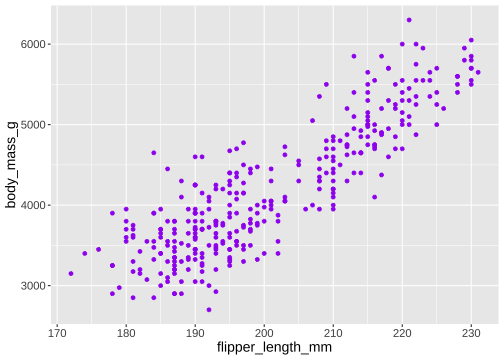
ggplot(penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species, shape = species)) + geom_point() + geom_density_2d()- Syntax starts with
geom_*. - eg: geom_histogram(), geom_bar(), geom_boxplot().
- Each shape has its own specific aesthetics arguments.
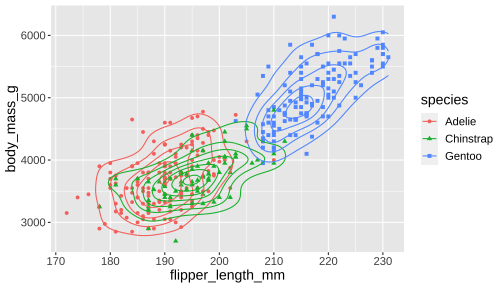
ggplot(penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species, shape = species)) + geom_point() + geom_density_2d()- Syntax starts with
geom_*. - eg: geom_histogram(), geom_bar(), geom_boxplot().
- Each shape has its own specific aesthetics arguments.

ggplot(penguins) + geom_histogram( aes(x = flipper_length_mm))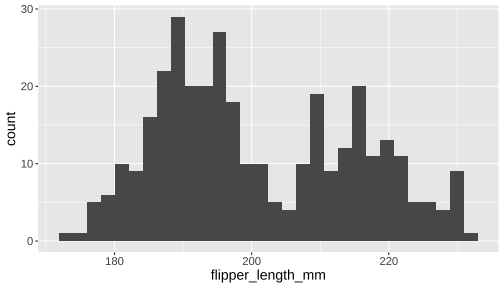
Each shape has its own specific aesthetics arguments.
?geom_point
Global Data vs Layer Specific Mapping
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point() + geom_density_2d()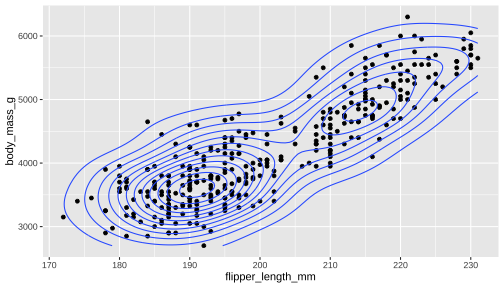
ggplot() + geom_point(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_density_2d()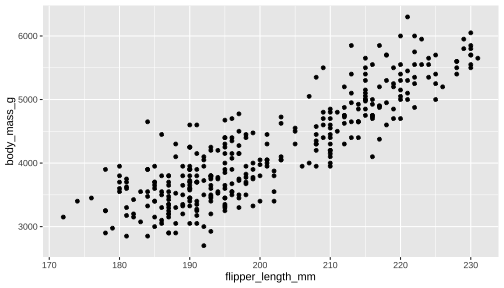
ggplot() + geom_point()
Global Data vs Layer Specific Mapping
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point() + geom_density_2d()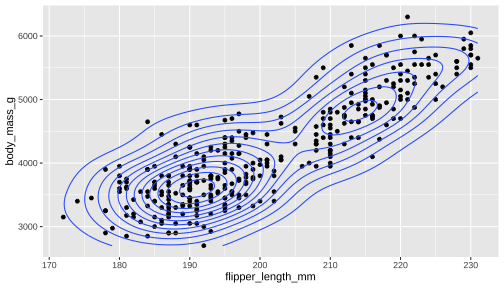
ggplot() + geom_point(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_density_2d(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g))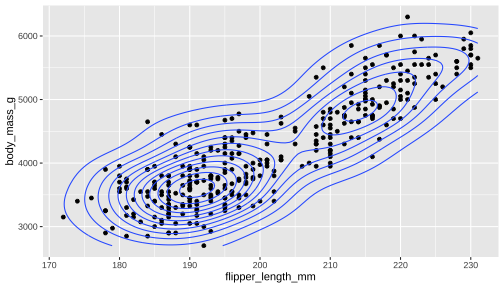
Statistics
- There are two ways to use statistical functions.
define stat_*() function and geom argument inside that function
ggplot(penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point() + stat_summary( geom ="point", fun.y ="mean", colour ="red")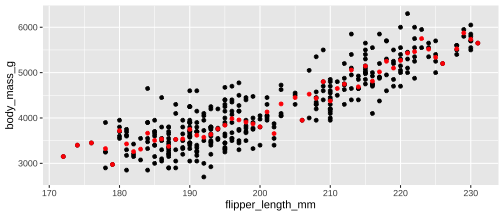
define geom_*() function and stat argument inside that function
ggplot(penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point() + geom_point( stat ="summary", fun.y ="mean", colour ="red")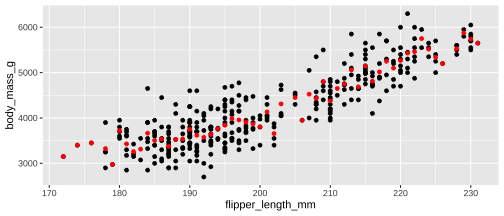
| Statistics | Geometries |
|---|---|
stat_count |
geom_bar |
stat_boxplot |
geom_boxplot |
stat_identity |
geom_col |
stat_bin |
geom_bar, geom_histogram |
stat_density |
geom_density |
| Statistics | Geometries |
|---|---|
stat_count |
geom_bar |
stat_boxplot |
geom_boxplot |
stat_identity |
geom_col |
stat_bin |
geom_bar, geom_histogram |
stat_density |
geom_density |
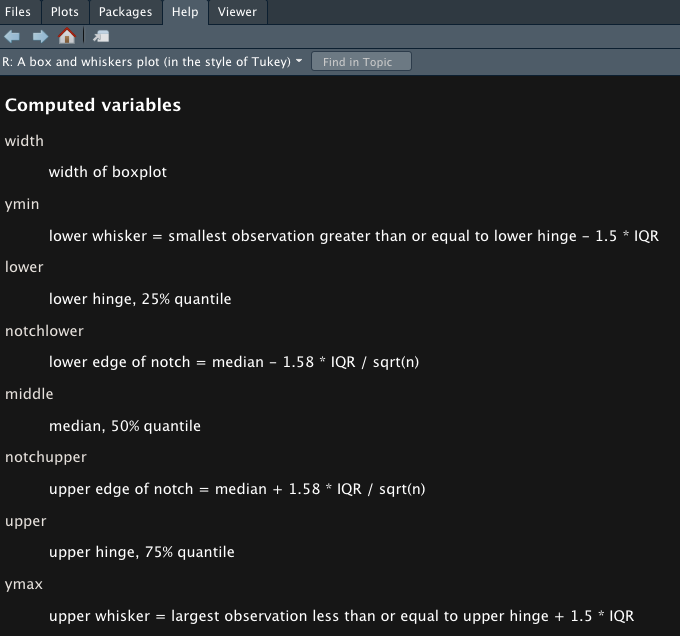
?geom_boxplot
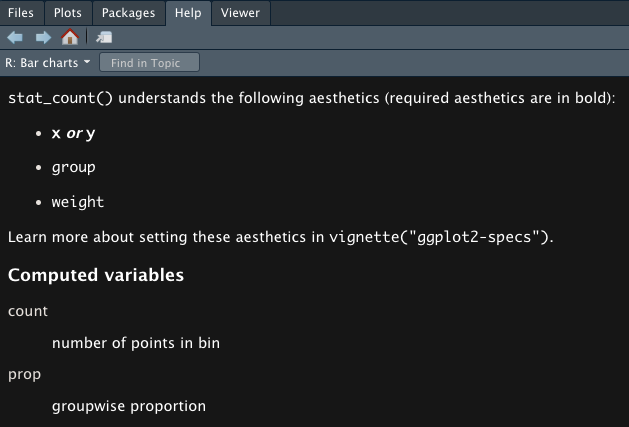
?geom_bar
Scales
Scales
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point( aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species, shape = species))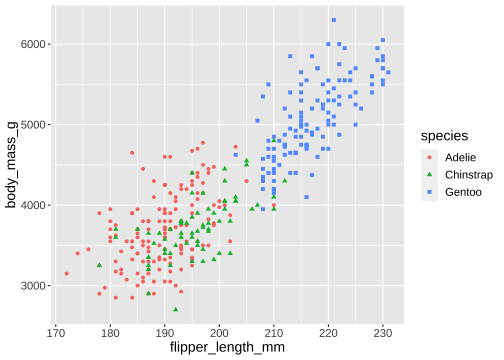
Scales
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point( aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species, shape = island))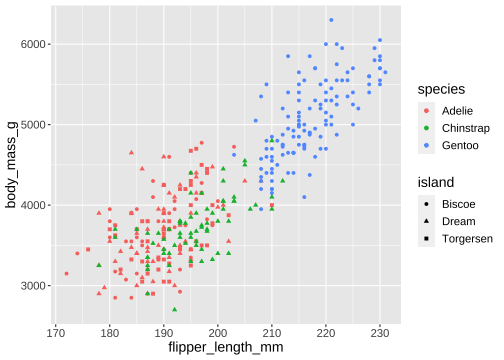
Scales manual
- It's recommended to use a named vector
cols <- c("Adelie" = "red", "Chinstrap" = "blue", "Gentoo" = "darkgreen")ggplot(penguins) + geom_point( aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species)) + scale_colour_manual(values = cols)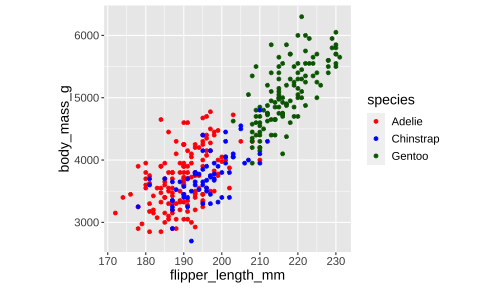
Scales
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point( aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = bill_length_mm, shape = island))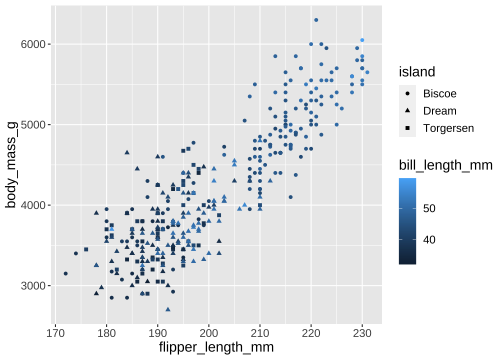
Scales
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species)) + scale_color_brewer(type = 'qual', palette = 'Dark2')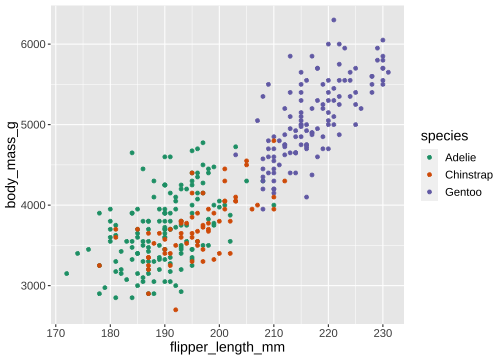
Scales
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species)) + scale_color_brewer(type = 'qual', palette = 'Dark2')
scale_<aesthetic>_<type>
RColorBrewer::display.brewer.all()
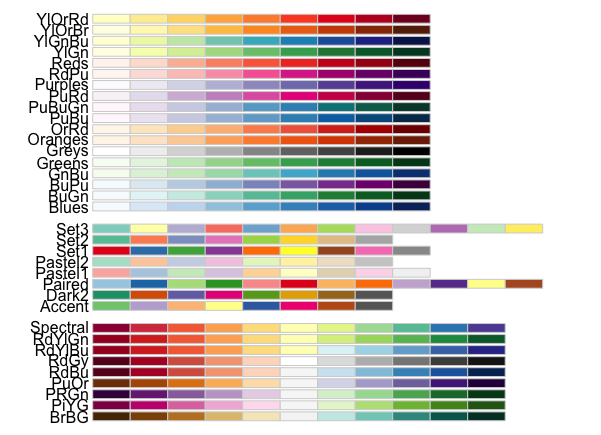
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species)) + scale_color_viridis_d()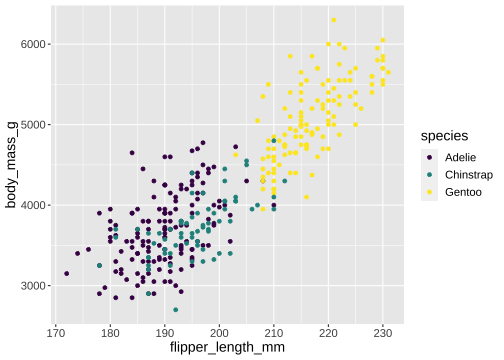
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species)) + scale_color_viridis_d()
viridisandRColorBrewerprovide different color scales that are robust to color-blindness.
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species)) + scale_color_viridis_d()
viridisandRColorBrewerprovide different color scales that are robust to color-blindness.- For details and an interactive palette selection tools see http://colorbrewer.org
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g, color = species, shape = species, alpha = species)) + scale_x_continuous( breaks = c(170,200,230)) + scale_y_log10() + scale_colour_viridis_d(direction = -1, option= 'plasma') + scale_shape_manual( values = c(17,18,19)) + scale_alpha_manual( values = c( "Adelie" = 0.6, "Gentoo" = 0.5, # "Chinstrap" = 0.7))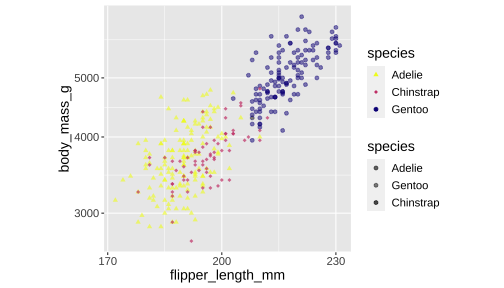
Facets
facet_wrap()
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes( x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + facet_wrap(vars(species))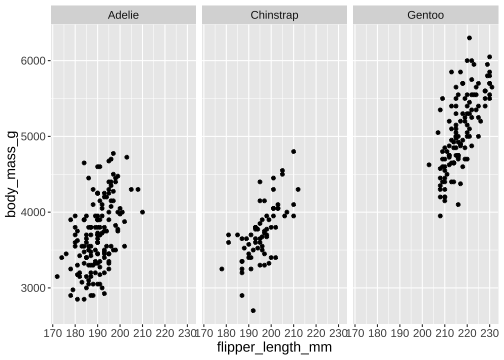
facet_wrap()
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes( x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + facet_wrap(vars(species), scales = "free_x")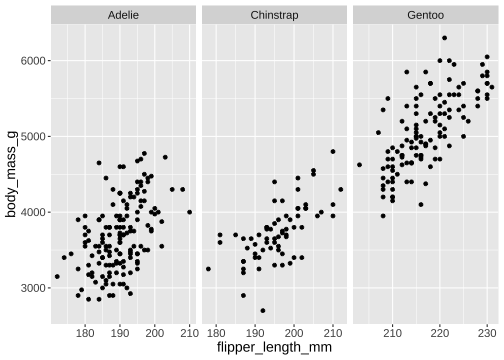
facet_grid()
ggplot(penguins) + geom_point(aes( x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + facet_grid( vars(species), vars(sex))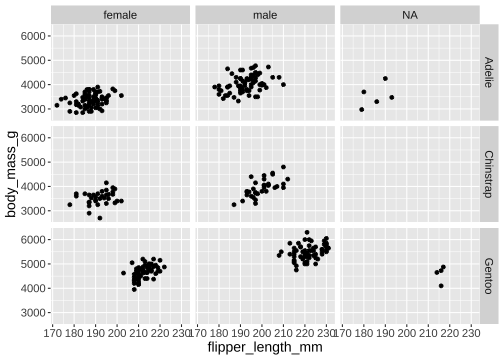
Coordinates
Coordinates
ggplot(penguins) + geom_bar(aes(x= species, fill = species))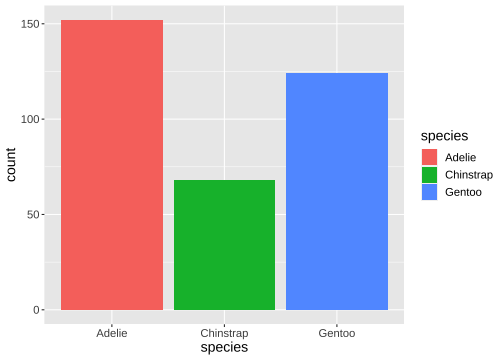
ggplot(penguins) + geom_bar(aes(x= species, fill = species)) + coord_flip()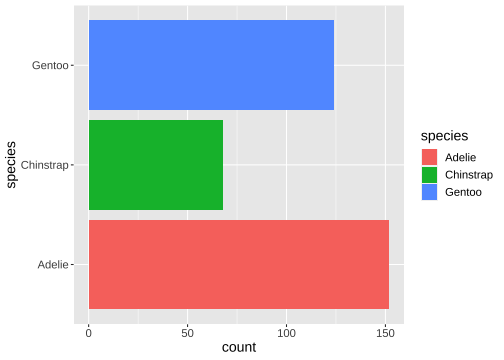
ggplot(penguins) + geom_bar(aes(x= species, fill = species)) + coord_flip()
- There are two types of coordinate systems:
- Linear coordinate systems
- Non-linear coordinate systems
ggplot(penguins) + geom_bar(aes(x= species, fill = species)) + coord_flip()
- There are two types of coordinate systems:
- Linear coordinate systems
- Non-linear coordinate systems
- Linear coordinate systems :
coord_cartesian(),coord_flip(),coord_fixed()
ggplot(penguins) + geom_bar(aes(x= species, fill = species)) + coord_flip()
- There are two types of coordinate systems:
- Linear coordinate systems
- Non-linear coordinate systems
- Linear coordinate systems :
coord_cartesian(),coord_flip(),coord_fixed() - Non-linear coordinate systems : eg :
coord_map(),coord_quickmap(),coord_sf(),coord_polar(),coord_trans()
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
- You Shouldn’t Use Pie Charts In Your Dashboards
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
- You Shouldn’t Use Pie Charts In Your Dashboards
- Many visualization software vendors no longer include them in their catalogs.
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
- You Shouldn’t Use Pie Charts In Your Dashboards
- Many visualization software vendors no longer include them in their catalogs.
- Pie charts are prone to misinterpretation and can easily be turned into disinformation.
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
- You Shouldn’t Use Pie Charts In Your Dashboards
- Many visualization software vendors no longer include them in their catalogs.
- Pie charts are prone to misinterpretation and can easily be turned into disinformation.
- Humans are not great at judging angles, which is exactly what a pie chart uses to represent size.
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
- You Shouldn’t Use Pie Charts In Your Dashboards
- Many visualization software vendors no longer include them in their catalogs.
- Pie charts are prone to misinterpretation and can easily be turned into disinformation.
- Humans are not great at judging angles, which is exactly what a pie chart uses to represent size.
- Lengths are much easier to compare, and length happens to be exactly what a bar chart uses to represent size.
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
- You Shouldn’t Use Pie Charts In Your Dashboards
- Many visualization software vendors no longer include them in their catalogs.
- Pie charts are prone to misinterpretation and can easily be turned into disinformation.
- Humans are not great at judging angles, which is exactly what a pie chart uses to represent size.
- Lengths are much easier to compare, and length happens to be exactly what a bar chart uses to represent size.
- Bar charts allows the viewer to make comparisons based on the the length of the bars along a common scale (the y-axis).
Accommodating Human Limitations
- Pie charts are one of the most overused graphs in the world and in most cases are not the best way to present data.
- You Shouldn’t Use Pie Charts In Your Dashboards
- Many visualization software vendors no longer include them in their catalogs.
- Pie charts are prone to misinterpretation and can easily be turned into disinformation.
- Humans are not great at judging angles, which is exactly what a pie chart uses to represent size.
- Lengths are much easier to compare, and length happens to be exactly what a bar chart uses to represent size.
- Bar charts allows the viewer to make comparisons based on the the length of the bars along a common scale (the y-axis).
- Humans tend to be more accurate when decoding differences based on these perceptual elements than based on area or color
Themes
These are complete themes which control all non-data display.
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point(aes( color = species, shape = species), size = 3, alpha = 0.8) + theme_minimal()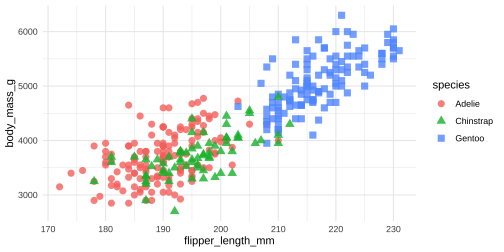
These are complete themes which control all non-data display.
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point(aes( color = species, shape = species), size = 3, alpha = 0.8) + theme_minimal()
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point(aes( color = species, shape = species), size = 3, alpha = 0.8) + theme_dark()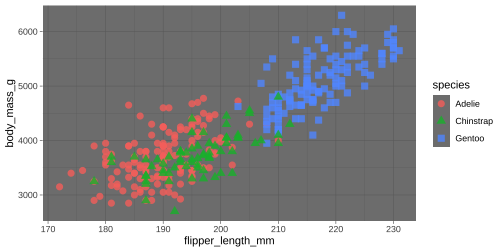
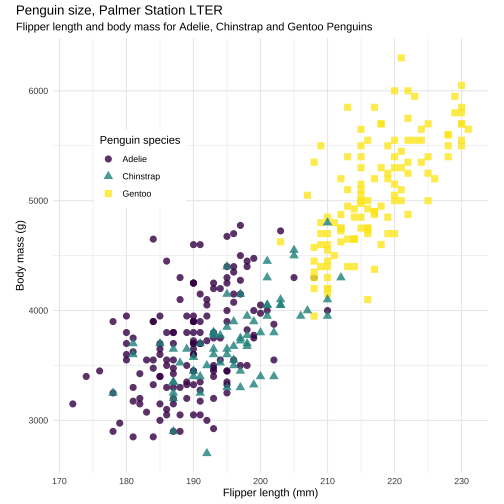
Create custom themes in ggplot.
ggplot(penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point(aes(color = species, shape = species), size = 3, alpha = 0.8) + scale_color_viridis_d() + theme_minimal() + labs( title = "Penguin size, Palmer Station LTER", subtitle = "Flipper length and body mass for Adelie, Chinstrap and Gentoo Penguins", x = "Flipper length (mm)", y = "Body mass (g)", color = "Penguin species", shape = "Penguin species") + theme( aspect.ratio = 1, legend.position = c(0.2, 0.7), legend.background = element_rect( fill = "white", color = NA), plot.title.position = "plot", plot.caption = element_text( hjust = 0, face= "italic"), plot.caption.position = "plot")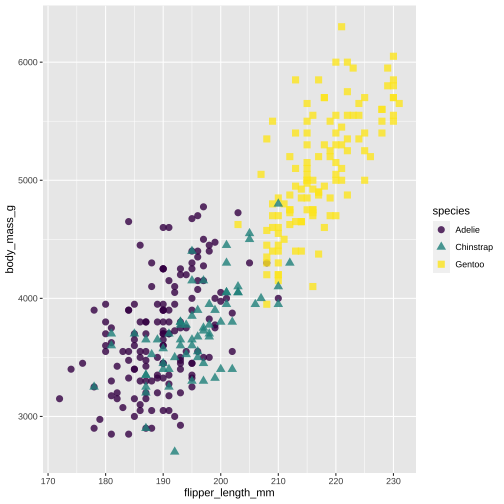
ggplot2 extensions
ggplot2 extensions: https://exts.ggplot2.tidyverse.org/
1. patchwork for plot composition

p1 <- ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm, y = body_mass_g)) + geom_point(aes(color = species, shape = species), size = 2) + scale_color_manual(values = c("darkorange","darkorchid","cyan4")) + theme(aspect.ratio = 1)p2 <- ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) + geom_point(aes(color = species, shape = species), size = 2) + scale_color_manual(values = c("darkorange","darkorchid","cyan4")) + theme(aspect.ratio = 1)p3 <- ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm)) + geom_histogram(aes(fill = species), alpha = 0.5, position = "identity") + scale_fill_manual(values = c("darkorange","darkorchid","cyan4"))library(patchwork)p1 + p3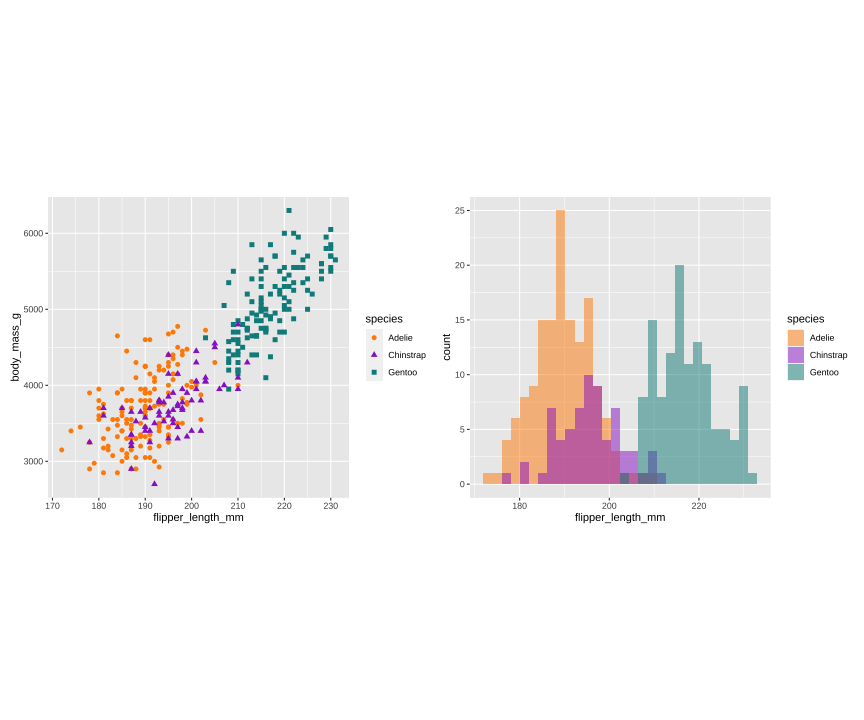
library(patchwork)(p1 | p2) / p3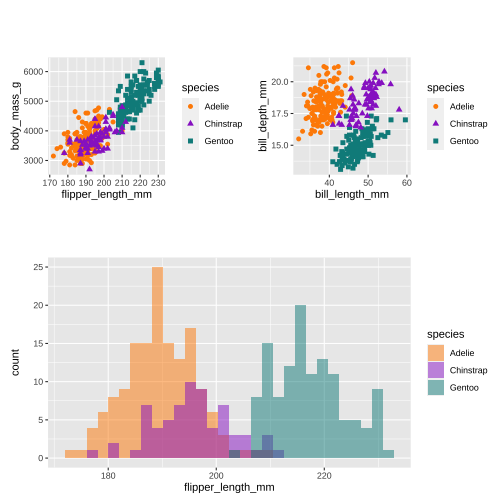
library(patchwork)p <- (p1 | p2) / p3p + plot_layout(guide = 'collect')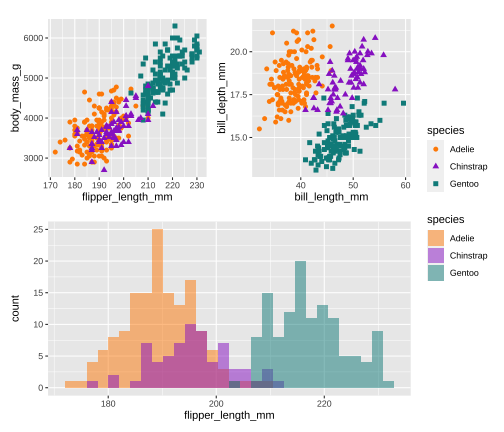
library(patchwork)p <- (p1 | p2) / p3p + plot_layout(guide = 'collect') + plot_annotation( title = 'Size measurements for adult foraging penguins near Palmer Station, Antarctica', tag_levels = 'A')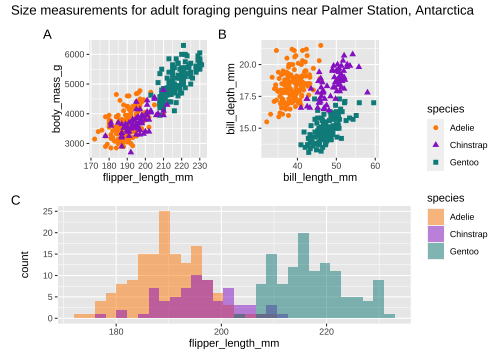
library(patchwork)p <- (p1 | p2) / p3p & theme(legend.position = 'none')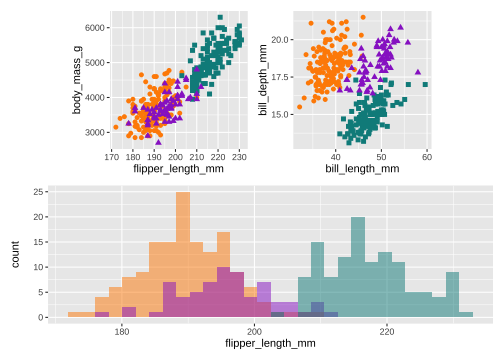
2. plotly
An R package for creating interactive web graphics via the open source JavaScript graphing library plotly.js.
p1 ## a ggplot object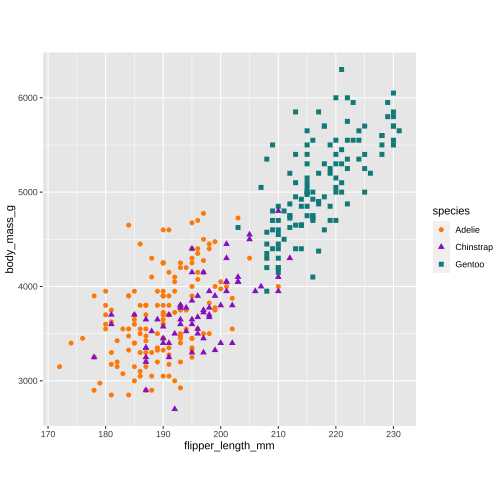
3. GGally
GGally::ggpairs(penguins[, 1:5], aes(color = species, fill = species))+ scale_color_viridis_d() + scale_fill_viridis_d()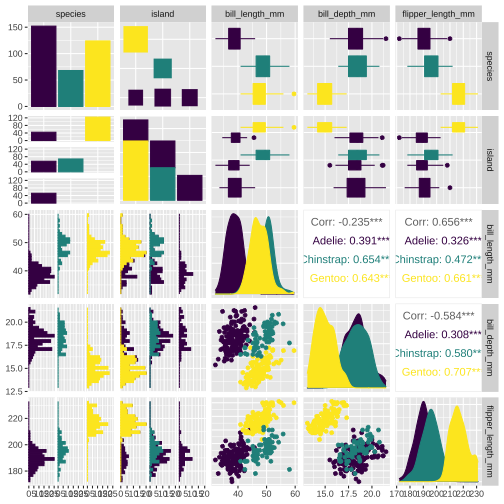
4. gganimate

library("ggplot2")library("dlstats")data <- cran_stats("ggplot2")p <- ggplot(data, aes(x= end, y = downloads)) + geom_line() + labs(title = "Download stats of ggplot2 package", x = "Time", y = "Downloads")p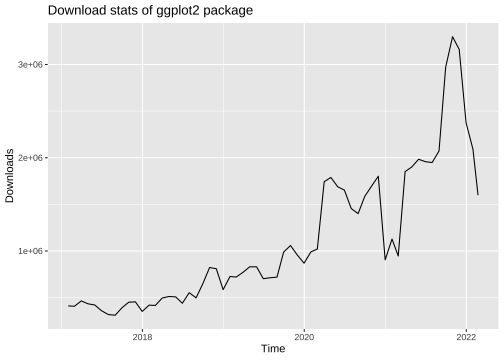
library(gganimate)p + transition_reveal(along = end)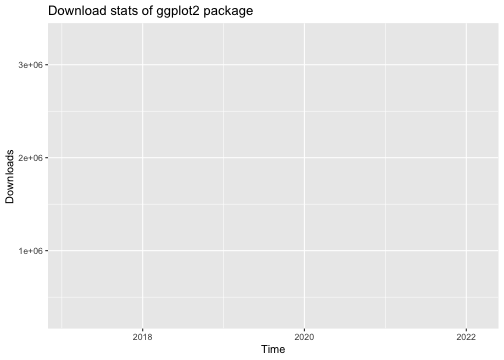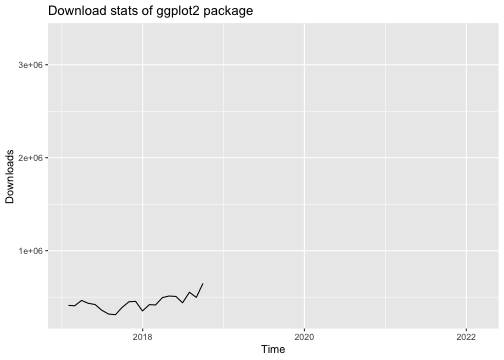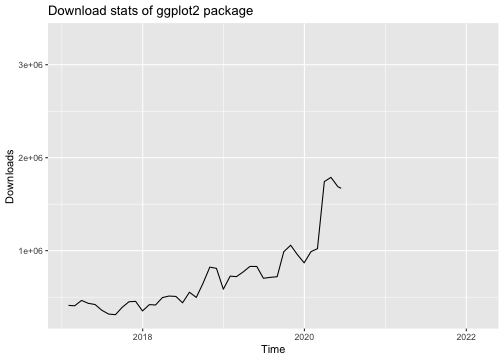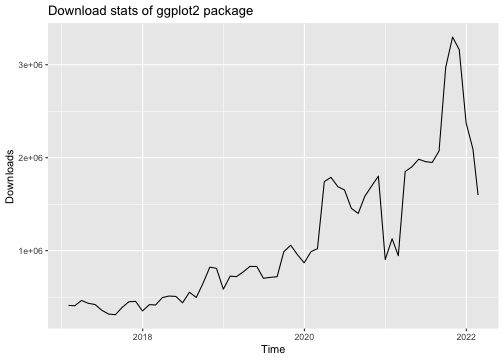
- Sometimes you might need to install the
pngandgifskipackages and restart the R-Studio.
p <- ggplot(penguins, aes(flipper_length_mm, body_mass_g , color = species)) + geom_point() + scale_color_viridis_d() + labs( title = "Measurements of penguins {closest_state}") + transition_states(states = year) + enter_grow() + exit_fade()p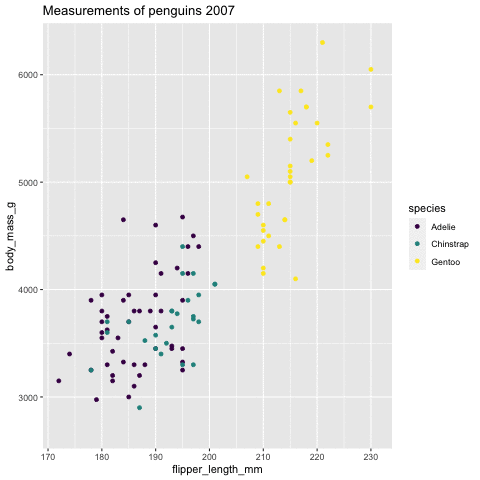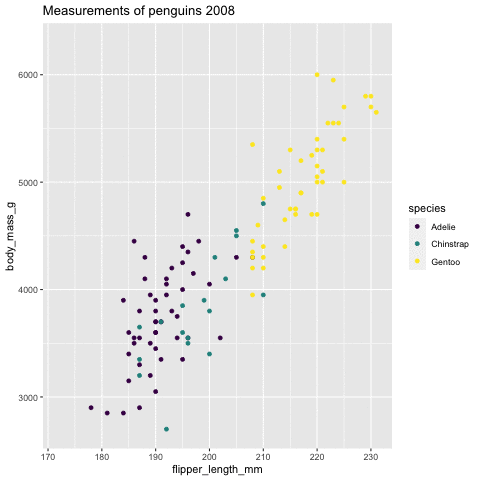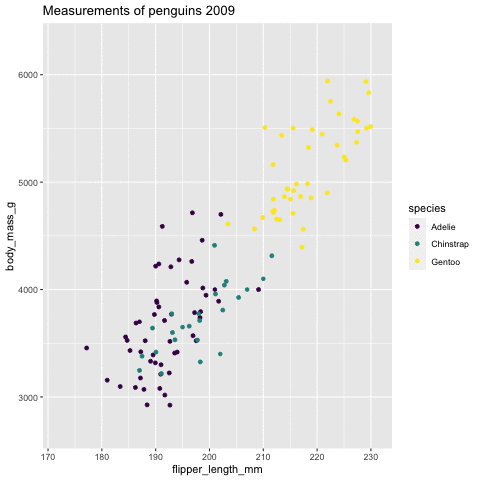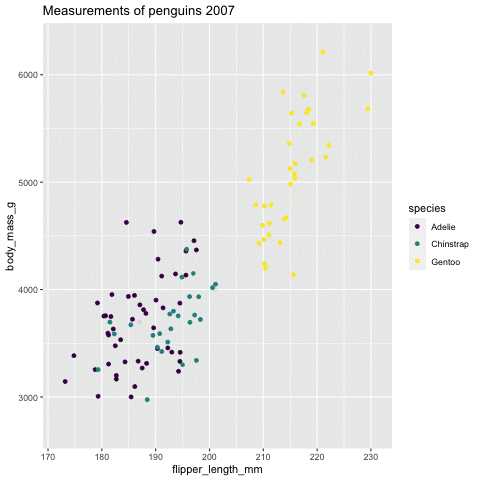
5. ggrepel

Text annotation
df <- penguins %>% filter( flipper_length_mm > 225 )ggplot(penguins, aes(x=flipper_length_mm, y= body_mass_g))+ geom_point()+ theme(aspect.ratio = 1) + geom_text(data= df, aes(x=flipper_length_mm, y= body_mass_g, label= island))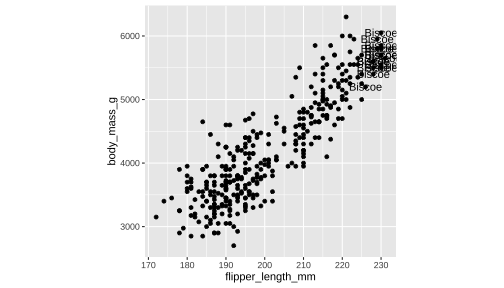
Text annotation
ggplot(penguins, aes(x=flipper_length_mm, y= body_mass_g))+ geom_point()+ theme(aspect.ratio = 1) + ggrepel::geom_text_repel(data= df, aes(x=flipper_length_mm, y= body_mass_g, label= island))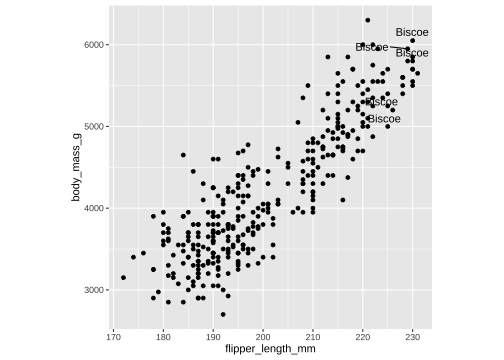
6. ggforce

library(ggforce)penguins <- penguins %>% drop_na()p <- ggplot(penguins, aes(x=flipper_length_mm, y= body_mass_g))+ geom_mark_ellipse(aes( filter = species == "Gentoo", label = 'Gentoo penguins'), description = 'Palmer Station Antarctica LTER and K. Gorman. 2020.') + geom_point() p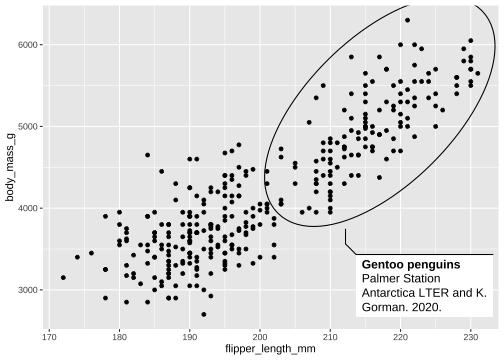
library(ggforce)ggplot(penguins, aes(x=flipper_length_mm, y= body_mass_g, color = species)) + geom_point() + scale_color_viridis_d() + facet_zoom(x = species == "Gentoo")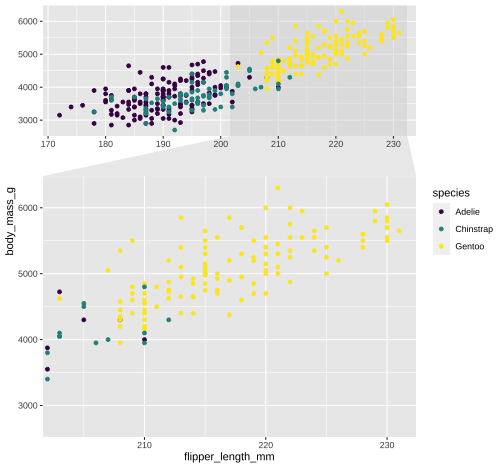
pridiltal and thiyangt
Acknowledgements:
Hadley Wickham, Thomas Lin Pedersen and ggplot development team
This work was supported in part by RETINA research lab funded by the OWSD, a program unit of United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
Key References
- ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis https://ggplot2-book.org/
- ggplot2 workshop by Thomas Lin Pedersen https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h29g21z0a68
All rights reserved by Thiyanga S. Talagala and Priyanga D Talagala